
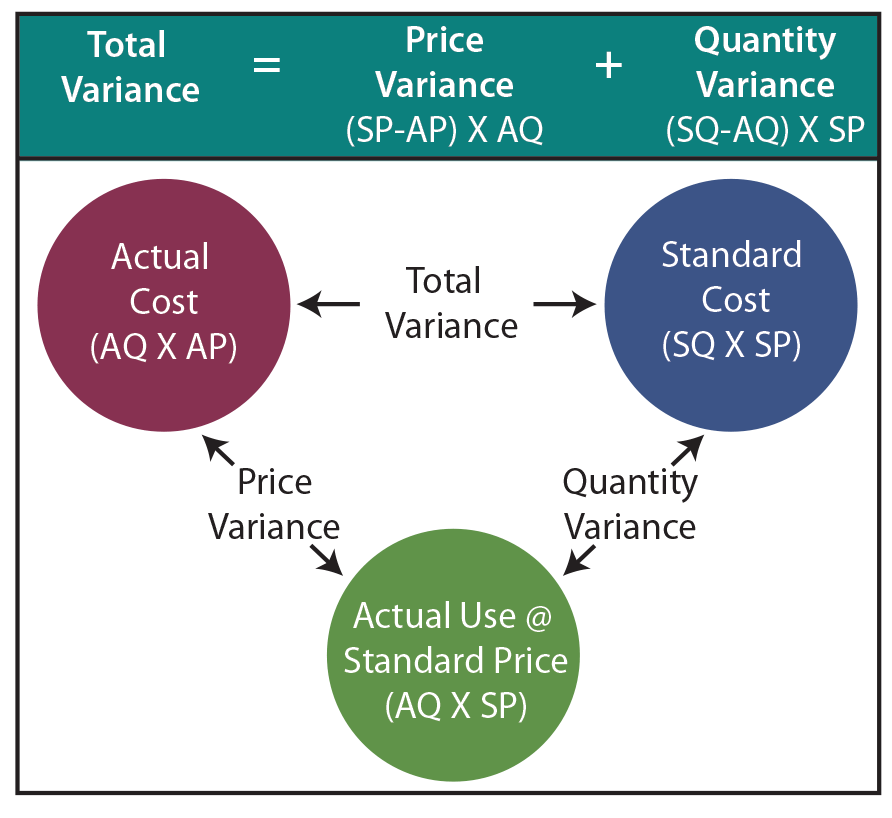
It also shows that the actual price per pound was $0.30 higher than standard cost (unfavorable). The direct materials used in production cost more than was anticipated, which is an unfavorable outcome. Direct material price variance (DM Price Variance) is defined as the difference between the expected and actual cost incurred on purchasing direct materials. It evaluates the extent to which the standard price has been over or under applied to different units of purchase.
Understanding the Material Quantity Variance
The normal wastage and inefficiencies are taken into account while setting direct materials price and quantity standards. Variances are calculated and reported at regular intervals to ensure the quick remedial actions against any unfavorable occurrence. In this case, the production department performed efficiently and saved 40 units of direct material. Multiplying this by the standard price per unit yields a favorable direct material quantity variance of $160. As businesses strive for greater precision in cost management, advanced techniques in variance analysis have become increasingly valuable. One such technique is the use of trend analysis, which involves examining variance data over multiple periods to identify patterns and trends.
Formula For Direct Materials Quantity Variance
The first step in this analysis is to regularly review variance reports, which provide a snapshot of how actual costs compare to standard costs. These reports should be detailed and timely, allowing managers to quickly identify and address any discrepancies. The difference between the standard cost of direct materials and the actual cost of direct materials that an organization uses for production is known as Material Variance. So let’s say that you were producing a good and had set standard costs for labor at $100 per good and the standard cost for materials at $200 per unit.
Quick Links
The first step in the calculation is to figure out how much stuffing material should be used to manufacture 9000 teddy bears (standard quantity). During a period, the Teddy Bear Company used 15,000 kilograms of stuffing material to produce 9000 teddy bears. Using the materials-related information given below, calculate how to professionally ask for payment from clients template the material variances for XYZ company for the month of October. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
- Dummies helps everyone be more knowledgeable and confident in applying what they know.
- Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
- Accountants typically use standard costing to estimate the value of direct materials, direct labor and manufacturing overhead in work-in-progress inventory.
- To determine the total PPV for a specific order, subtract the standard amount from the actual amount.
- Managers can better address this situation if they have a breakdown of the variances between quantity and price.
Calculator for Direct Material Price Variance
The materials price variance can be computed either when materials are purchased or when they are placed into production. The standard rates calculated for batch and product level activities do not vary with production volume. This example illustrates the accounting entries for purchase price variance and exchange rate variance for a standard cost item.
How is direct materials price variance calculated?
To calculate direct materials, add beginning direct materials to direct materials purchases and subtract ending direct materials. For example, say that a company had $3,000 worth of flour stock at the beginning of the year, bought $10,000 worth of flour during the year, and has $2,000 worth of flour remaining at year end. We compared standard cost to the ability of a household to budget food costs for a month. Through this, we saw how it acts both as a guideline for appropriate spending habits for those who may not purchase routinely, as well as a better way to plan for future spending.
Understanding the factors that influence direct material variance is essential for businesses aiming to maintain control over their production costs. Market conditions, geopolitical events, and changes in supply and demand can all cause fluctuations in material costs. For instance, a sudden increase in the price of steel due to international trade policies can lead to an unfavorable material price variance for manufacturers relying on this resource. Companies must stay informed about market trends and consider strategies such as hedging or long-term contracts to mitigate these risks. With our direct material price variance calculator, we aim to help you assess the difference between the actual cost of direct materials and the standard cost.
This cross-functional collaboration ensures that all aspects of the business are aligned towards achieving cost efficiency. If there wasn’t enough supply available of the necessary raw materials, the company purchasing agent may have been forced to buy a more expensive alternative. If the company bought a smaller quantity of raw materials, they may not have qualified for favorable bulk pricing rates. In other words, if the business has consumed fewer materials to produce a given level of output than expected, the material quantity variance is said to be favorable. The material quantity variance in this example is favorable because the company manufactured the output using a lesser quantity of materials than what was planned in the budget. Direct materials quantity variance is also known as direct material usage or volume variance.
This is the difference between the standard and actual cost per unit of the direct materials purchased, multiplied by the standard number of units expected to be used in the production process. To calculate the direct material quantity variance, we measure the difference between the standard cost of materials that should have been used to produce the actual level of output and the standard cost of the actual quantity of materials used. If a company’s actual quantity used exceeds the standard allowed, then the direct materials quantity variance will be unfavorable. This means that the company has utilized more materials than expected and may have paid extra in materials cost.
The difference between the expected and actual cost incurred on purchasing direct materials, expressed as a positive or negative value, evaluated in terms of currency. The material quantity variance is a subset of the quantity variance, since it only applies to materials (or, more accurately, direct materials) that are used in the production process. Reliable suppliers who consistently deliver quality materials at agreed-upon prices help maintain stable production costs. Conversely, issues such as late deliveries, substandard materials, or unexpected price hikes can lead to variances. Building strong relationships with suppliers and regularly evaluating their performance can help businesses anticipate and address potential problems before they impact production. Together with the price variance the quantity variance forms part of the total direct materials variance.
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. The material quantity variance is also known as the material usage variance and the material yield variance. Of course, variances can be caused by production snafus, such as an excessive amount of scrap while setting up a production run, or perhaps damage caused by mishandling.





