
You can now use this information and the TIE formula provided above to calculate Company W’s time interest earned ratio. EBIT is used primarily because it gives a more accurate picture of the revenues that are available to fund a company’s interest payments. how to report backdoor roth in turbotax Welcome to our Times Interest Earned Ratio Calculator – Your tool for assessing financial stability. Input EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) and Interest Expense, and our calculator will help you estimate the Times Interest Earned Ratio.
Calculating Times Interest Earned
The times interest earned ratio shows how many times a company can pay off its debt charges with its earnings. If a company has a ratio between 0.90 and 1, it means that its earnings are not able to pay off its debt and that its earnings are less than its interest expenses. To have a detailed view of your company’s total interest expense, here are other metrics to consider apart from times interest earned ratio.
Standard Deviation Percentile Calculator
A TIE ratio of less than 1 indicates that the company is not generating enough earnings to cover its interest expenses, which could be a red flag for investors. Conversely, a TIE ratio above 2 is generally considered healthy, suggesting that the company can comfortably meet its interest obligations. In that case, it means the company is not generating enough to pay the interest on its loans and might have to dig into the cash reserves, affecting company liquidity. EBIT is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from total revenues, excluding interest and taxes.
Understanding the Times Interest Earned Ratio
This metric, also known as the interest coverage ratio, provides insight into how easily a firm can pay the interest on its outstanding debt. Investors consider it one of the most critical debt ratio and profitability ratios because it can help you determine if a company is likely to go bankrupt beforehand. Calculating the Times Interest Earned Ratio is crucial for assessing a company’s ability to cover its interest payments with its earnings. This financial metric offers insights into a company’s financial health and creditworthiness. Our Times Interest Earned Ratio Calculator simplifies this calculation for you. The times interest earned (TIE) ratio is a financial metric that measures a company’s ability to fulfill its interest obligations on outstanding debt.
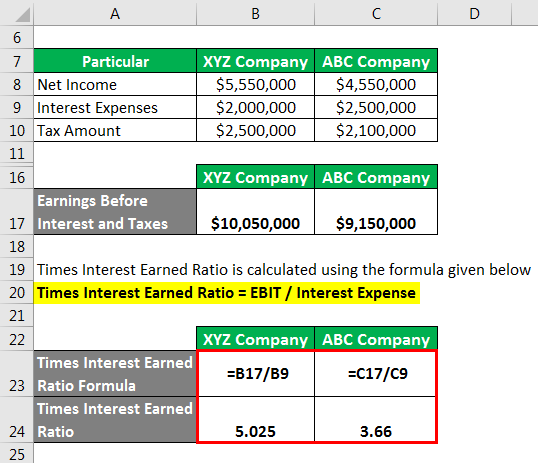
- The times interest earned spreadsheet calculator is available for download in Excel format by following the link below.
- Yes, the TIE ratio can vary significantly depending on the industry.
- Interest expense and income taxes are often reported separately from the normal operating expenses for solvency analysis purposes.
- This metric, also known as the interest coverage ratio, provides insight into how easily a firm can pay the interest on its outstanding debt.
- So try to match as much as possible competitors, considering, for example, the level of revenues.
Definition – What is Time Interest Earned Ratio?
With that said, it’s easy to rack up debt from different sources without a realistic plan to pay them off. If you find yourself with a low times interest earned ratio, it should be more alarming than upsetting. This ratio determines whether you are in a position to pay the interest to the venture capitalists for fundraising with your retained earnings. Hence, it is required to find a financial ratio to link earnings before interests and taxes with the interest the company needs to pay. With it, you can not only track when a company is earning more money than the interest it has to pay but also when the earnings are getting worse and the risk of credit default is increasing. The Times Interest Earned (TIE) Ratio measures a company’s ability to meet its debt obligations by comparing its earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) to its interest expenses.
Understanding the TIE ratio
Another aspect to be considered is the similarity in business models and company size. A large and settled one will likely experience less volatility in their earnings than a small/mid company. So try to match as much as possible competitors, considering, for example, the level of revenues. In short, it indicates the level of safety that a company has for debt interest repayment.
In most cases, higher Times Interest Earned (TIE) means your company has more cash. The times interest earned ratio is a calculation that allows you to examine a company’s interest payments, in order to determine how capable it is of meeting its debt obligations in a timely fashion. The different debt analysis tools, such as current ratio calculator and the quick ratio calculator, are complementary to the interest coverage ratio calculator because they show different information. The latter focuses on cash inflows and outflows rather than on current assets and current liabilities like the former one.
This number measures your revenue, taking all expenses and profits into account, before subtracting what you expect to pay in taxes and interest on your debts. As a rule of thumb, investors generally look to have at least an interest coverage ratio greater than 3. In other words, we are looking for companies that are currently earning (before paying interest and taxes) at least three times what they have to pay in interest. Is the TIE ratio the same as the debt service coverage ratio (DSCR)?
The company’s shareholders expect an annual dividend payment of 8% plus growth in the stock price of XYZ. By analyzing TIE in conjunction with these metrics, you get a better understanding of the company’s overall financial health and debt management strategy. If you have three loans generating interest and don’t expect to pay those loans off this month, you must plan to add to your debts based on these different interest rates. This additional amount tacked onto your debts is your interest expense. The higher the TIE, the better the chances you can honor your obligations. A TIE ratio of 5 means you earn enough money to afford 5 times the amount of your current debt interest — and could probably take on a little more debt if necessary.
Rising interest rates increase interest expenses, which can lower the TIE ratio, while falling interest rates reduce interest expenses, potentially raising the ratio. Our team of experts continuously updates and expands our calculator library, ensuring that you have access to the latest and most relevant tools for your specific needs. There’s certainly a fine balance to Times Interest Earned. It’s important to consider all financial indicators as you gauge your health.





